Is ECG a roadmap to reach the heart?
Ever wondered about the importance of ECG in life? An ECG (electrocardiogram) is a graphical representation of the recording of the electrical activity of the heart occurring during the cardiac cycle. It is used especially in diagnosing abnormalities of the cardiac cycle. In other words, ECG can be referred to as electrical tracing of the heart. It is a compilated record of action potentials produced by all the heart muscle fibres during each heartbeat. Willem Einthoven first invented the ECG in 1902. The word ‘ECG’ is derived from In German term, it is elektro-kardiographie (EKG).
ECG is also abbreviated as EKG.
Image Source: Principles of Anatomy and Physiology By Gerard J. Tortora, Bryan H. Derrickson
Table of Contents
Components of electrocardiograph machine
-
Electrodes (sensors)- There is a set of recording electrodes called leads and these are connected to a power amplifier.
- It has a silver quartz string vertically suspended between the poles of a horseshoe-shaped electromagnet.
-
Gauze and skin preparation (alcohol rub) solution
-
Razors or clippers or a roll of tape (for hair removal)
-
Skin adhesive and/or antiperspirant
-
Cardiac monitor or electrocardiography machine
- The amplified signals are fed to the writing system and the tracings are recorded on ECG graph paper.
Image Source: www.indiamart.com
Principle behind ECG (electrocardiogram)
Image Source: https://ecglibrary.com
The ECG machine works mostly by the detection and amplification of the electrical changes on the skin. These are caused due to heart muscle depolarization during each heartbeat. The electrical changes are particularly conducted through body fluids to the body surface and these can be picked up by the electrodes of the ECG machine.
Process of obtaining ECG (electrocardiogram)
i) A specialised gel is applied on the chest of the patient that has the role to allow electrical conduction. A brief history of allergy to these gels are also checked.
ii) A patient is connected to the ECG machine along with three electrical leads. Two leads to each wrist and one to the left ankle.
iii) Many other leads are also attached to the chest of the patient.
Interpretation of ECG
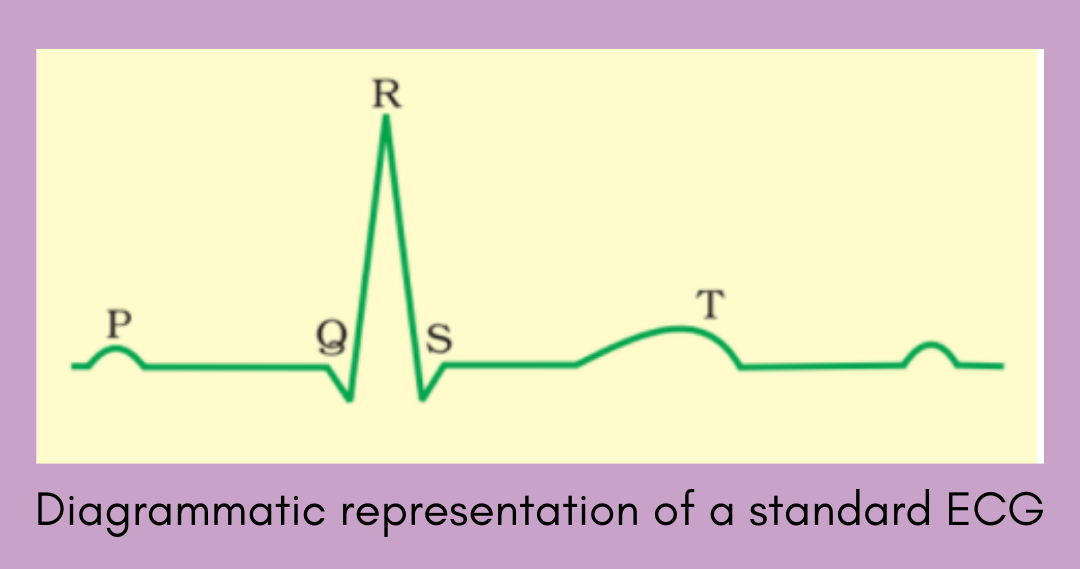
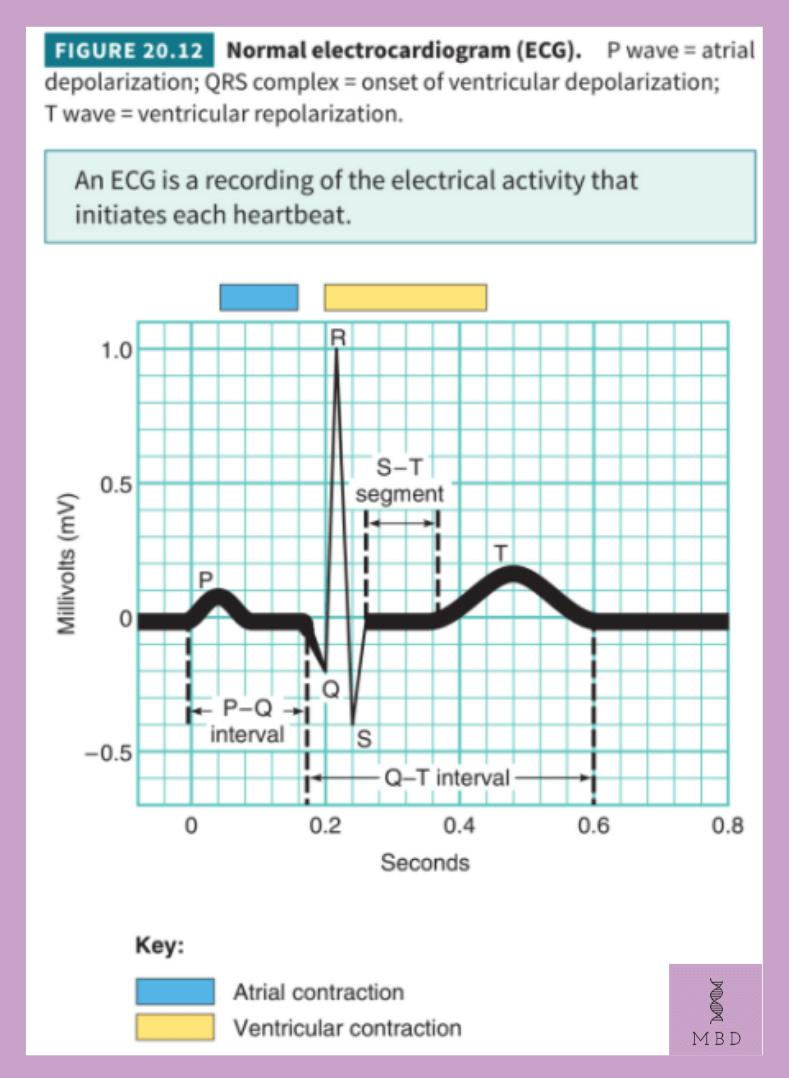
Each peak in the ECG (electrocardiogram) is identified with a letter from P to T that corresponds to a specific electrical activity of the heart. ECG can be interpreted using the following points-
- The P-wave particularly represents the electrical excitation (depolarization) of the atria, which leads to the contraction of both the atria. It is a small upward deflection in the ECG.
- The QRS complex represents the depolarization of the ventricles, which initiates ventricular contraction. The contraction starts shortly after Q and marks the beginning of the systole.
- The T-wave represents the return of the ventricles from an excited to a normal state (repolarisation).
- The end of the T-wave marks the end of the systole.
One cardiac cycle is from the start of the P wave to the end of the T wave.
Image Source: NCERT
Any deviation from this shape of ECG indicates a possible abnormality or disease leading to an abnormal ECG.
- A larger P wave indicates enlargement of an atrium.
- A deep and wide Q wave may indicate a myocardial infarction.
- An enlarged R wave generally indicates enlarged ventricles.
- The T wave is flatter than normal, it indicates the heart muscle is receiving insufficient oxygen. This is seen in coronary artery disease.
- The T wave may be elevated in high blood potassium level-hyperkalemia.
Clinical significance of ECG
The overall goal of performing an ECG is to obtain information about the electrical functioning of the heart. By comparing the records of a person with normal records, it is possible to determine the following things-
- If the heart rate is more or less than normal (Tachycardia and Bradycardia respectively)
- If the heart chambers are enlarged
- The cause of chest pain.
Some indications when ECG should be performed include the following:
-
- Chest pain or suspected myocardial infarction, for instance in ST elevated myocardial infarction (STEMI).
- Medication monitoring in cardiac diseases.
A flattened line in the ECG means that the person is dead.
To summarize, do remember – “Life is like an ECG; if there are no ups and downs in your life, it means you are dead.”
Hope the article could very well explain to you the importance of ECG (electrocardiogram) in life.
Thank you for reading at MBD.
For more: My Biology Dictionary – MY BIOLOGY DICTIONARY



Quite knowledgeable..!!
Looking for more such content in future